Introduction

Personal finance isn’t just about counting pennies or stashing away savings—it’s the deliberate and strategic practice of steering your money with clarity and confidence. At its core, personal finance is the skill of aligning your current financial behaviors with your future ambitions. Whether it’s buying your dream home, launching a passion-fueled business, or securing a stress-free retirement, everything begins with understanding how your money actually works for (or against) you.
In an age where expenses seem to rise faster than salaries and financial choices have multiplied into a dizzying array of credit cards, apps, and investment options, financial literacy has evolved from a nice-to-have into a survival skill. Today, being good with money means more than knowing how to save—it means knowing when to save, where to invest, how to protect your wealth, and most importantly, how to spend with purpose.
This guide dives deep into the five foundational pillars of personal finance: managing income, budgeting effectively, saving wisely, investing smartly, and protecting your assets. Think of these not just as financial habits, but as building blocks for lifelong resilience. Whether you’re a complete beginner, overwhelmed by jargon, or someone seeking a fresh, simplified framework—you’re in the right place.
By the end of this journey, you won’t just know what personal finance is; you’ll feel empowered to take action, make informed decisions, and move closer to a life where money supports your goals rather than controls them.
The 5 Basics of Personal Finance
Personal finance is much more than balancing a check book or setting aside spare change at the end of the month. It’s a dynamic, lifelong process of managing your money in a way that supports both your present lifestyle and your future aspirations. In a world of increasing financial complexity—where expenses rise and opportunities are endless—having a solid financial strategy is not just smart; it’s essential.
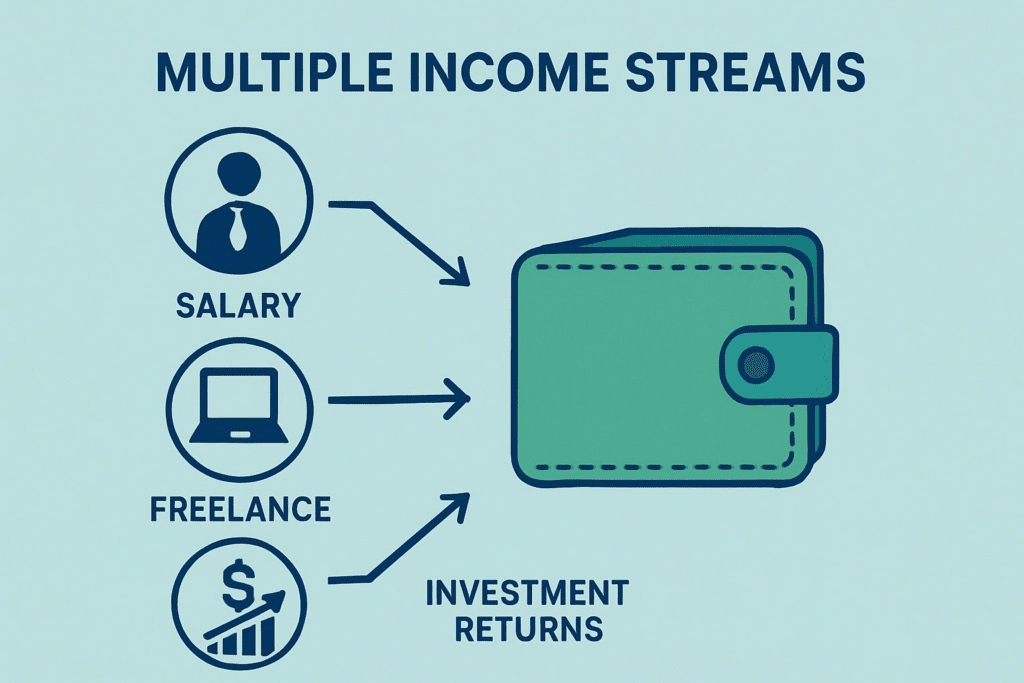
To navigate this journey successfully, there are five foundational principles that every individual, regardless of age or income level, should understand. These aren’t just steps—they’re interconnected tools designed to help you gain control, reduce stress, and build long-term wealth.
1. Income Management: Know What You Earn and Make It Work for You
The starting point of any financial plan is understanding your income—not just how much you make, but where it comes from, how consistent it is, and how you can improve it. Most people rely heavily on a single stream of income, usually a job. But true financial security often comes from diversification—freelance work, passive income, or even small investments that grow over time.
Once you’re aware of all your income sources, it’s time to optimize. This might mean pursuing higher-paying roles, building a side hustle, or investing in skills that increase your earning potential. When you actively manage your income, you stop working for your money—and start making your money work for you.
2. Budgeting: Give Every Dollar a Job
A budget isn’t a restriction; it’s a roadmap. It helps you decide in advance how to allocate your money based on what matters most to you. Whether you’re using a spreadsheet, an app, or the classic envelope system, the goal remains the same: spend with intention.
Popular frameworks like the 50/30/20 rule offer a simple starting point—half your income goes to needs, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings or debt repayment. But the real magic happens when you review and refine your budget regularly. As your life evolves, so should your financial plan.
3. Saving: Build Your Financial Safety Net
Saving is your defense against life’s inevitable curveballs. A solid savings habit is what separates those who panic in a crisis from those who pivot with ease. Start with an emergency fund that covers 3 to 6 months of living expenses—this creates a cushion against job loss, medical emergencies, or unexpected repairs.
From there, focus on goal-oriented savings: a vacation, a car, a home down payment, or your child’s education. Automating your savings is a game changer. When the money moves before you can spend it, saving becomes effortless and consistent.
4. Investing: Grow Your Wealth, Don’t Just Store It
If saving is defensive, investing is offense. It’s how you grow your money faster than inflation can eat it away. While it might feel risky at first, especially if you’re new to it, investing is one of the most powerful tools for achieving long-term financial independence.
Start small, start smart. Index funds and ETFs offer beginner-friendly options with broad diversification and low fees. As your confidence grows, you can explore more complex strategies, but the key is to begin. Time in the market matters far more than timing the market, and even modest investments can grow significantly over the years thanks to compound interest.
5. Protection: Safeguard What You’re Building
All the planning and effort in the world can be undone by a single unexpected event—an illness, an accident, or a lawsuit. That’s why protection is an often overlooked yet crucial pillar of personal finance. This includes having the right insurance coverage: health, life, disability, renters or homeowners, and auto. It also means creating legal safeguards like a will, power of attorney, and emergency instructions.
Financial protection isn’t paranoia—it’s preparedness. It ensures that your finances and your loved ones are shielded from the unknown, allowing you to move through life with greater peace of mind.
Why These Principles Matter More Than Ever
These five areas—income management, budgeting, saving, investing, and protection—form the core of a strong financial life. They’re not isolated tasks to check off a list, but a system that works best when all parts are in motion. When you treat personal finance as a lifelong skill set, you stop simply reacting to money problems and start proactively designing the life you want.
The truth is, you don’t need to be wealthy to master personal finance—but mastering personal finance can absolutely lead to wealth. More importantly, it leads to confidence, freedom, and peace of mind—things money can’t buy, but smart money habits can build.
Why These Basics Matter
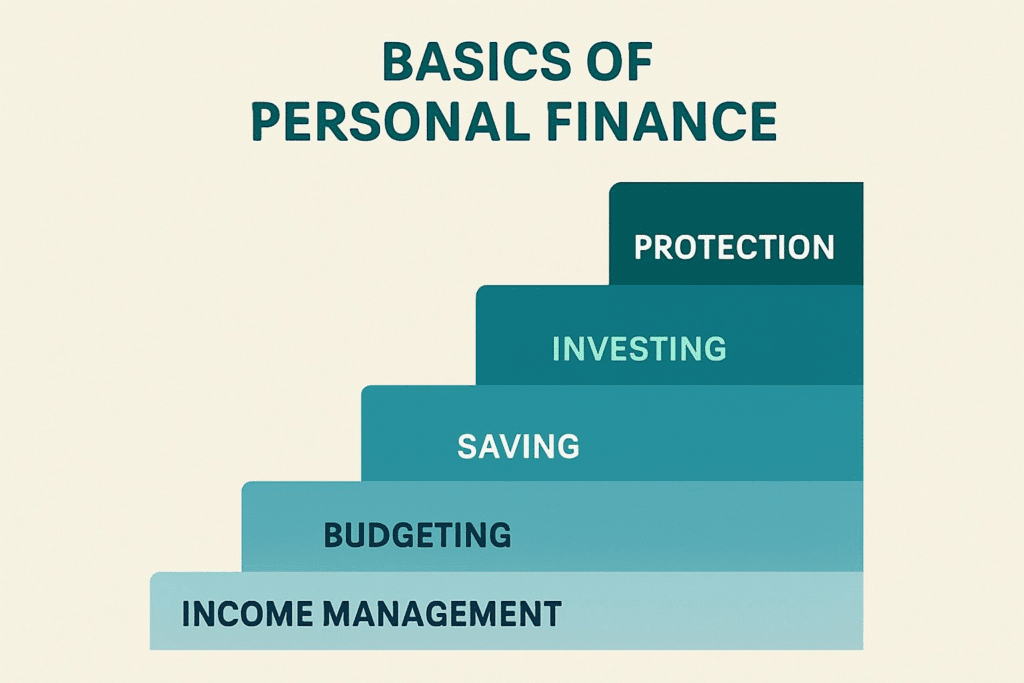
The five basics of personal finance—income management, budgeting, saving, investing, and protection—are more than fundamental ideas. They are practical instruments that enable you to create a strong financial base, achieve independence, and unlock long-term growth. Here’s why gaining mastery over these core areas is essential:
1. They Create a Foundation of Financial Stability
When you understand how much money you bring in and how you’re spending it, you start to take control instead of reacting to financial pressure. A smart budget keeps your spending aligned with your goals, and building an emergency fund cushions you against unexpected costs. These habits work together to reduce stress, prevent living paycheck to paycheck, and bring greater peace of mind.
2. They Prepare You for the Life You Want
Long-term planning becomes possible when you regularly save and make thoughtful investments. Whether you’re aiming to purchase a house, fund a passion project, or retire early, having a financial roadmap puts those dreams within reach. Protection tools like insurance and estate planning ensure that, even in life’s unexpected moments, your future and your family’s well-being remain secure.
3. They Empower Smarter Decision-Making
Knowing the basics helps you cut through confusion and take confident action. Instead of guessing when faced with financial choices—like selecting an investment, handling debt, or increasing income—you’ll have the knowledge to assess risks and opportunities clearly. Financial literacy turns complex decisions into manageable ones.
4. They Drive Long-Term Financial Growth
Investing isn’t just for the wealthy—it’s how wealth is built. As your knowledge expands, you’ll be able to explore investment options suited to your goals and risk tolerance. Over time, your money starts to work for you, compounding and growing beyond what simple saving can offer. With the right strategy, financial independence becomes a destination rather than a dream.
5. They Build the Resilience to Withstand Uncertainty
No one can predict the future, but you can prepare for it. A solid savings habit, combined with appropriate insurance and protection plans, allows you to face emergencies without derailing your financial health. Resilience means that setbacks don’t become crises—and that you remain on course even when life throws you off balance.
Mastering these five financial fundamentals puts you in the driver’s seat of your life. They’re not just good practices—they’re the difference between financial stress and financial strength.
How to Implement These Basics
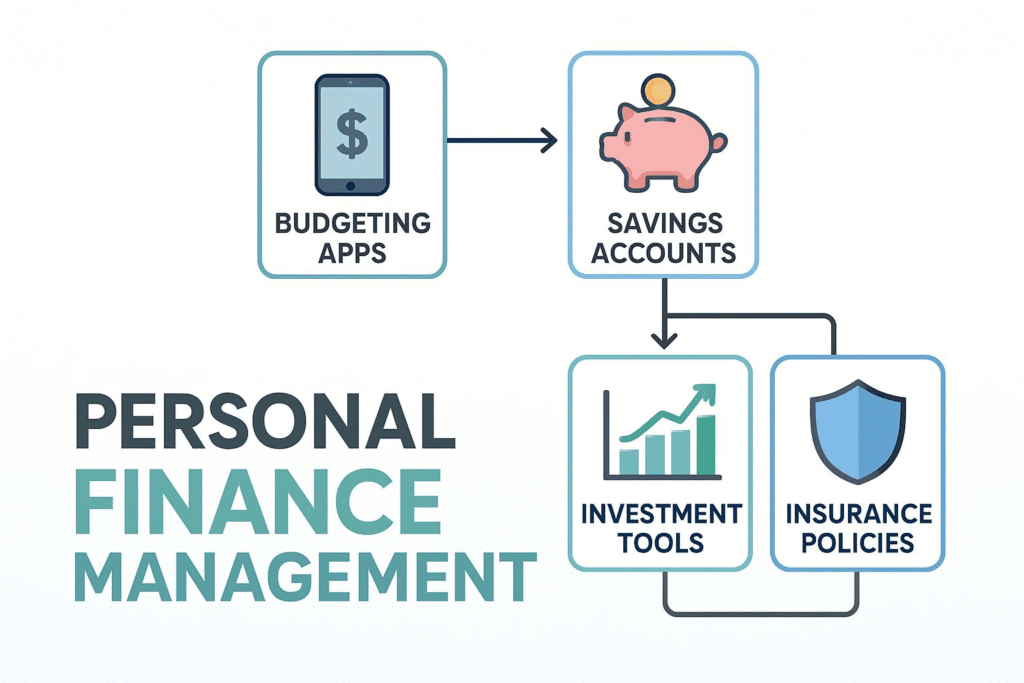
Understanding the core concepts of personal finance is just the beginning—the real impact comes from turning knowledge into consistent action. Here’s how you can bring these five financial basics to life in your everyday routine:
1. Income Management
- Track Every Source: Use digital tools or a simple spreadsheet to record not just your main salary, but all income—from side gigs, passive earnings, or dividends. Knowing your full financial picture is empowering.
- Increase Your Potential: Look for new ways to grow your income, whether through freelancing, upskilling, or negotiating a raise. Your earning power is often your greatest financial asset.
- Keep Evaluating: Periodically assess how your income sources are performing and stay open to adjustments that can make them more efficient or profitable.
2. Budgeting
- Begin with a Simple Framework: Use the 50/30/20 rule as a starting point—allocate 50% of your income to essentials, 30% to personal wants, and 20% toward savings or debt repayment.
- Use Smart Tools: Apps like YNAB (You Need A Budget) or Mint can automate your tracking and help you visualize spending patterns over time.
- Adapt as You Go: Your life changes, and your budget should too. Revisit your budget monthly and tweak it based on new goals or changes in income and expenses.
3. Saving
- Build a Safety Net: Make it a priority to save three to six months of living costs in a separate, easily accessible account to cushion against emergencies.
- Make Saving Automatic: Set up recurring transfers from your main account to your savings—automation makes it easier to stay disciplined without thinking about it.
- Define Your Purpose: Set clear, achievable savings goals for things like a vacation, education, or retirement. Purpose-driven saving keeps you motivated and focused.
4. Investing
- Take Small, Smart Steps: Start with low-cost, beginner-friendly options like ETFs or index funds to gain experience while minimizing risk.
- Spread the Risk: Don’t rely on just one type of investment. Diversify your portfolio across different sectors and asset classes to build resilience.
- Keep Learning: Read trusted financial books, attend webinars, or take beginner investment courses to sharpen your knowledge and make better-informed decisions.
5. Protection
- Understand What You Need: Evaluate your lifestyle and responsibilities to decide which types of insurance are most essential—health, life, disability, property, etc.
- Choose Wisely: Shop around and compare insurance policies. Aim for coverage that balances protection and affordability without unnecessary extras.
- Plan for the Future: Secure your legacy with a will or trust to ensure your assets are managed according to your wishes, giving your loved ones peace of mind.
Consistency is the Secret Ingredient
Financial success doesn’t come from one-off efforts—it’s built through steady, intentional action. Check in with your finances regularly, refine your strategies as life evolves, and seek expert guidance when you face unfamiliar territory. When you stay consistent, these personal finance basics transform from good ideas into powerful habits—and eventually, into real financial freedom.
Conclusion
Grasping and applying the five essential pillars of personal finance—managing income, budgeting wisely, saving consistently, investing thoughtfully, and protecting what you’ve built—is the gateway to long-term financial health. These aren’t just tips—they’re tools for designing a life with fewer financial surprises and more freedom to pursue what truly matters to you.
The good news? You don’t need a drastic overhaul to begin. Lasting financial success comes from steady, manageable actions. From creating your first budget to setting up automatic savings or dipping your toes into investing, each small decision compounds over time, leading to powerful results.
Financial literacy isn’t a one-time achievement—it’s an evolving skill set that grows with you. As you continue to apply these fundamentals, you’ll become better equipped to make informed choices, adapt when challenges arise, and take advantage of opportunities with confidence. The goal isn’t just to “get by”—it’s to build a life that’s financially secure, independent, and aligned with your goals.
There’s no perfect time to start—but there is value in starting now. Take that first, simple step. Stay consistent. Let these five financial basics become the habits that reshape your future. Your path to financial freedom starts today
FAQ’s
Why is budgeting important in personal finance?
Budgeting helps you take control of your finances by providing a clear plan for your income and expenses. It ensures you live within your means, allocate money for savings, and avoid unnecessary debt. A good budget is the foundation for achieving both short-term and long-term financial goals
How much should I save for emergencies?
It’s recommended to have an emergency fund that covers 3–6 months of living expenses. This provides a financial safety net to handle unexpected situations like medical emergencies, job loss, or major repairs without disrupting your financial stability.
What are the best investment options for beginners?
For beginners, low-risk options such as index funds, ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds), or government bonds are a great starting point. These investments are relatively stable and provide diversification, which reduces risk. Always research or seek professional advice before investing.
Do I need insurance if I’m young and healthy?
Yes, insurance is essential regardless of age or health. Health insurance protects you from high medical costs, and life insurance can provide financial support for dependents in case of unforeseen circumstances. Starting early also ensures lower premiums over time.
How can I track my income and expenses effectively?
You can use apps like Mint, YNAB (You Need A Budget), or PocketGuard to monitor your cash flow. Alternatively, a simple spreadsheet works well for tracking income and expenses. Regularly reviewing these records helps you stay on top of your financial situation.